- Steel making
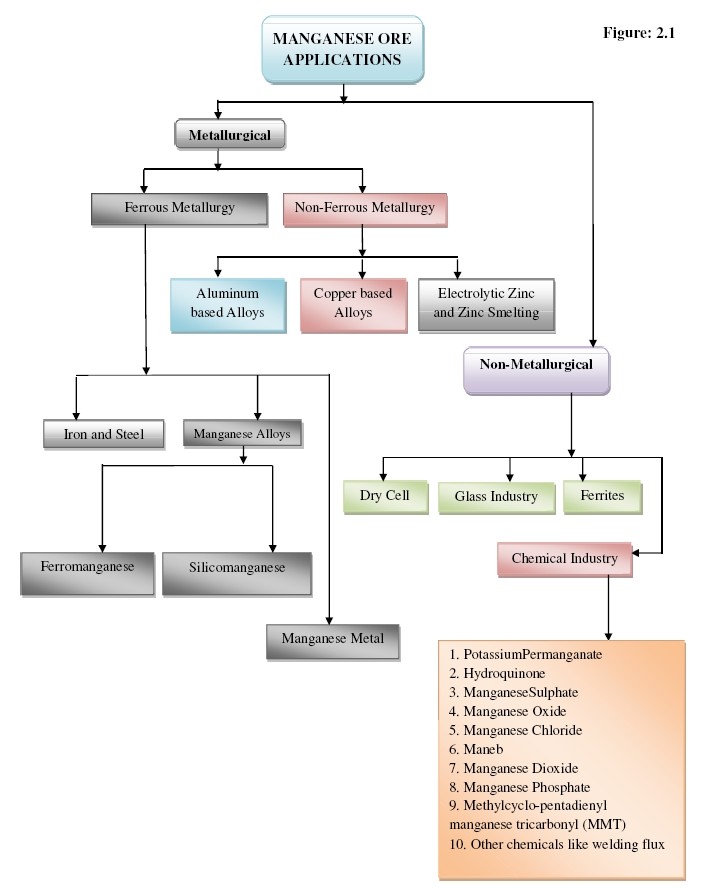
 At present steel making accounts for 85% to 90% of total manganese consumption. Manganese is often used by the steel industry in deoxidizing and desulfurizing additives and as an alloying constituent. It can improve the rolling and forging qualities, as well as the strength, toughness, stiffness, hardness, wear resistance, and hardenability of steels. For example, steel containing 8-15% manganese can have a high tensile strength of up to 863 MPa, and steel with 12% or more manganese is used in applications in which great toughness and wear resistance is required, such as gyratory crushers, jaw-crusher plates, railway points and crossover components.
At present steel making accounts for 85% to 90% of total manganese consumption. Manganese is often used by the steel industry in deoxidizing and desulfurizing additives and as an alloying constituent. It can improve the rolling and forging qualities, as well as the strength, toughness, stiffness, hardness, wear resistance, and hardenability of steels. For example, steel containing 8-15% manganese can have a high tensile strength of up to 863 MPa, and steel with 12% or more manganese is used in applications in which great toughness and wear resistance is required, such as gyratory crushers, jaw-crusher plates, railway points and crossover components.- Aluminum alloys
 The second large application for manganese is as an alloying agent for aluminum. Aluminum with a manganese content of about 1.5% has an increased resistance against corrosion due to the formation of grains absorbing impurities which would lead to galvanic corrosion. Aluminum-manganese alloys have been applied in various products such as beverage cans, kitchenware, roofing, car radiators and transportation.
The second large application for manganese is as an alloying agent for aluminum. Aluminum with a manganese content of about 1.5% has an increased resistance against corrosion due to the formation of grains absorbing impurities which would lead to galvanic corrosion. Aluminum-manganese alloys have been applied in various products such as beverage cans, kitchenware, roofing, car radiators and transportation.- Copper alloys
 Manganese is probably the most versatile element that can be added to copper alloys. Small additions of manganese (0.1% to 0.3%) are used to deoxidize the alloy and improve its castability and mechanical strength. Manganese has a high solid solubility in copper and in binary systems with copper and aluminum, zinc or nickel as the binary constituent. Many commercial copper alloys contain around 1% to 2% manganese to improve strength and hot workability. Far higher levels of manganese content are found in some alloys for specific applications, for example, one alloy (72% Mn, 18% Cu, 10% Ni) is used for bimetallic strips in temperature control devices fitted to cars and other vehicles. However, copper alloys consume only two million tonnes of manganese per year and hence provide a limited market for manganese.
Manganese is probably the most versatile element that can be added to copper alloys. Small additions of manganese (0.1% to 0.3%) are used to deoxidize the alloy and improve its castability and mechanical strength. Manganese has a high solid solubility in copper and in binary systems with copper and aluminum, zinc or nickel as the binary constituent. Many commercial copper alloys contain around 1% to 2% manganese to improve strength and hot workability. Far higher levels of manganese content are found in some alloys for specific applications, for example, one alloy (72% Mn, 18% Cu, 10% Ni) is used for bimetallic strips in temperature control devices fitted to cars and other vehicles. However, copper alloys consume only two million tonnes of manganese per year and hence provide a limited market for manganese.- Other metal alloys
 Manganese is also used in other metal alloys. An alpha-beta titanium-base alloy contains 8% manganese and was used for the Gemini re-entry control module in the 1960s. Some zinc alloys and magnesium alloys also contain 0.1% to 0.2% manganese. Manganese can also be added to gold, silver, bismuth etc., to produce alloys which are used for very specific applications, generally related to the electronic industry. However, manganese used in these metal alloys accounts for a small percentage of the total manganese demand.
Manganese is also used in other metal alloys. An alpha-beta titanium-base alloy contains 8% manganese and was used for the Gemini re-entry control module in the 1960s. Some zinc alloys and magnesium alloys also contain 0.1% to 0.2% manganese. Manganese can also be added to gold, silver, bismuth etc., to produce alloys which are used for very specific applications, generally related to the electronic industry. However, manganese used in these metal alloys accounts for a small percentage of the total manganese demand.
- Batteries
 The most important non-metallurgical application of manganese is in the form of manganese dioxide, which is used as a depolarizer in dry-cell batteries. The function of the manganese dioxide in batteries is to oxidize the hydrogen and form water. The Leclanché cell, which was first developed in 1868, incorporated this process and used manganese dioxide as the depolarizer. Alkaline batteries, which were put on the market in the 1950s, are a type of primary batteries dependent upon the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (Zn/MnO2). Another cell used specifically for military applications is the magnesium chloride-manganese dioxide cell.
The most important non-metallurgical application of manganese is in the form of manganese dioxide, which is used as a depolarizer in dry-cell batteries. The function of the manganese dioxide in batteries is to oxidize the hydrogen and form water. The Leclanché cell, which was first developed in 1868, incorporated this process and used manganese dioxide as the depolarizer. Alkaline batteries, which were put on the market in the 1950s, are a type of primary batteries dependent upon the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (Zn/MnO2). Another cell used specifically for military applications is the magnesium chloride-manganese dioxide cell.- Naturally occurring manganese dioxides (NMD) can be used in standard cells. Improved manganese dioxide grades required in high performance cells are obtained synthetically. The products are named after the processes used. EMD, or electrochemical manganese dioxide, is made through electrolysis; CMD, or chemical manganese dioxide, is produced by a purely chemical process. Combined production of both synthetic types is approximately 300,000 tonnes per year, and is growing rapidly. The major producing countries of natural MnO2 are Gabon, Ghana, Brazil, China, Mexico and India. These “natural grade battery” ores are ground into a fine powder before being used directly in the cathode mixture.
- Chemicals
 Manganese compounds have been used in many chemical fields. For example, permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used in quantitative analysis and in medicine. Potassium permanganate is used to purify drinking water and treat waste water. It is also used as disinfectant for treating skin disease.
Manganese compounds have been used in many chemical fields. For example, permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used in quantitative analysis and in medicine. Potassium permanganate is used to purify drinking water and treat waste water. It is also used as disinfectant for treating skin disease.- Another important application for manganese is “Maneb” (manganese-ethylene bisdithiocarbamate), an organo-chemical compound which is sold as an agricultural fungicide and is widely used for controlling crop and cereal diseases, downy mildew in vines, scab in fruit trees, banana and peanut diseases. Manganese sulphate is widely used as an end product in fertilizers and animal feed, and as an intermediate product in the chemical industry.
- An organic manganese compound called MMT (methylcyclo-pentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl) has been used as an octane booster or anti-knock agent in unleaded gasoline. MMT can greatly improve oil combustion, reducing boiler clogging and soot levels. This application is important in view of environmental protection because it allows lead to be replaced, but it has not yet been fully developed.
- Manganese dioxide is used in drying black paints and in the preparation of oxygen and chlorine. It also acts as a catalyst in the production of artificial flavors like vanilla and as an oxidizing agent in treating uranium ore to produce the oxide-concentrate. Manganese compounds have also been used in the coloring of ceramics and glass.
- Manganese compounds have also been used in the coloring of ceramics and glass.
- Other applications
- Manganese phosphatation is used to produce surface films which, when sealed with oil or wax, can protect steels for internal or mild outdoor use. Manganese phosphating improves wear resistance, prevents welding of metals under load, increases lubrication efficiency by oil absorption and assures rapid and safe running-in of moving parts.
- Manganese ferrite is widely used in electronics and a large quantity goes into producing television circuit boards.
-
About us
Contact us
Make a suggestion
- Metalpedia is a non-profit website, aiming to broaden metal knowledge and provide extensive reference database to users. It provides users reliable information and knowledge to the greatest extent. If there is any copyright violation, please notify us through our contact details to delete such infringement content promptly.
 At present steel making accounts for 85% to 90% of total manganese consumption. Manganese is often used by the steel industry in deoxidizing and desulfurizing additives and as an alloying constituent. It can improve the rolling and forging qualities, as well as the strength, toughness, stiffness, hardness, wear resistance, and hardenability of steels. For example, steel containing 8-15% manganese can have a high tensile strength of up to 863 MPa, and steel with 12% or more manganese is used in applications in which great toughness and wear resistance is required, such as gyratory crushers, jaw-crusher plates, railway points and crossover components.
At present steel making accounts for 85% to 90% of total manganese consumption. Manganese is often used by the steel industry in deoxidizing and desulfurizing additives and as an alloying constituent. It can improve the rolling and forging qualities, as well as the strength, toughness, stiffness, hardness, wear resistance, and hardenability of steels. For example, steel containing 8-15% manganese can have a high tensile strength of up to 863 MPa, and steel with 12% or more manganese is used in applications in which great toughness and wear resistance is required, such as gyratory crushers, jaw-crusher plates, railway points and crossover components. The second large application for manganese is as an alloying agent for aluminum. Aluminum with a manganese content of about 1.5% has an increased resistance against corrosion due to the formation of grains absorbing impurities which would lead to galvanic corrosion. Aluminum-manganese alloys have been applied in various products such as beverage cans, kitchenware, roofing, car radiators and transportation.
The second large application for manganese is as an alloying agent for aluminum. Aluminum with a manganese content of about 1.5% has an increased resistance against corrosion due to the formation of grains absorbing impurities which would lead to galvanic corrosion. Aluminum-manganese alloys have been applied in various products such as beverage cans, kitchenware, roofing, car radiators and transportation. Manganese is probably the most versatile element that can be added to copper alloys. Small additions of manganese (0.1% to 0.3%) are used to deoxidize the alloy and improve its castability and mechanical strength. Manganese has a high solid solubility in copper and in binary systems with copper and aluminum, zinc or nickel as the binary constituent. Many commercial copper alloys contain around 1% to 2% manganese to improve strength and hot workability. Far higher levels of manganese content are found in some alloys for specific applications, for example, one alloy (72% Mn, 18% Cu, 10% Ni) is used for bimetallic strips in temperature control devices fitted to cars and other vehicles. However, copper alloys consume only two million tonnes of manganese per year and hence provide a limited market for manganese.
Manganese is probably the most versatile element that can be added to copper alloys. Small additions of manganese (0.1% to 0.3%) are used to deoxidize the alloy and improve its castability and mechanical strength. Manganese has a high solid solubility in copper and in binary systems with copper and aluminum, zinc or nickel as the binary constituent. Many commercial copper alloys contain around 1% to 2% manganese to improve strength and hot workability. Far higher levels of manganese content are found in some alloys for specific applications, for example, one alloy (72% Mn, 18% Cu, 10% Ni) is used for bimetallic strips in temperature control devices fitted to cars and other vehicles. However, copper alloys consume only two million tonnes of manganese per year and hence provide a limited market for manganese. Manganese is also used in other metal alloys. An alpha-beta titanium-base alloy contains 8% manganese and was used for the Gemini re-entry control module in the 1960s. Some zinc alloys and magnesium alloys also contain 0.1% to 0.2% manganese. Manganese can also be added to gold, silver, bismuth etc., to produce alloys which are used for very specific applications, generally related to the electronic industry. However, manganese used in these metal alloys accounts for a small percentage of the total manganese demand.
Manganese is also used in other metal alloys. An alpha-beta titanium-base alloy contains 8% manganese and was used for the Gemini re-entry control module in the 1960s. Some zinc alloys and magnesium alloys also contain 0.1% to 0.2% manganese. Manganese can also be added to gold, silver, bismuth etc., to produce alloys which are used for very specific applications, generally related to the electronic industry. However, manganese used in these metal alloys accounts for a small percentage of the total manganese demand. The most important non-metallurgical application of manganese is in the form of manganese dioxide, which is used as a depolarizer in dry-cell batteries. The function of the manganese dioxide in batteries is to oxidize the hydrogen and form water. The Leclanché cell, which was first developed in 1868, incorporated this process and used manganese dioxide as the depolarizer. Alkaline batteries, which were put on the market in the 1950s, are a type of primary batteries dependent upon the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (Zn/MnO2). Another cell used specifically for military applications is the magnesium chloride-manganese dioxide cell.
The most important non-metallurgical application of manganese is in the form of manganese dioxide, which is used as a depolarizer in dry-cell batteries. The function of the manganese dioxide in batteries is to oxidize the hydrogen and form water. The Leclanché cell, which was first developed in 1868, incorporated this process and used manganese dioxide as the depolarizer. Alkaline batteries, which were put on the market in the 1950s, are a type of primary batteries dependent upon the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (Zn/MnO2). Another cell used specifically for military applications is the magnesium chloride-manganese dioxide cell. Manganese compounds have been used in many chemical fields. For example, permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used in quantitative analysis and in medicine. Potassium permanganate is used to purify drinking water and treat waste water. It is also used as disinfectant for treating skin disease.
Manganese compounds have been used in many chemical fields. For example, permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used in quantitative analysis and in medicine. Potassium permanganate is used to purify drinking water and treat waste water. It is also used as disinfectant for treating skin disease.
