- As the tungsten industry is continuously improving, consumption of tungsten resources is also increasing. Therefore, tungsten recycling has become the focus of this industry. In fact, the recycling of tungsten scrap isn't a modern procedure. On the contrary, it has been established for many years and plays an important part in the world’s tungsten supply. It is estimated that today about 30% of tungsten scrap is recycled every year, and the tungsten processing industry can recycle almost every kind of tungsten-containing scrap and waste and, if present, other valuable constituents.
 There are several reasons for recycling tungsten scrap. First, most scrap materials are richer in tungsten than ore concentrations, making tungsten scrap a worthy material for recycling. Second, the demand for tungsten products is increasing; consequently, the demand for tungsten resources is rising. Companies can lower their raw material costs and make greater profits by recycling tungsten scrap. Third, recycling tungsten scrap has many environmental benefits, such as reducing land-filled waste, saving valuable and finite virgin raw materials and energy, as well as reducing pollution.
There are several reasons for recycling tungsten scrap. First, most scrap materials are richer in tungsten than ore concentrations, making tungsten scrap a worthy material for recycling. Second, the demand for tungsten products is increasing; consequently, the demand for tungsten resources is rising. Companies can lower their raw material costs and make greater profits by recycling tungsten scrap. Third, recycling tungsten scrap has many environmental benefits, such as reducing land-filled waste, saving valuable and finite virgin raw materials and energy, as well as reducing pollution. Methods for recycling tungsten can be broadly divided into two types: direct methods and indirect methods. Direct methods mean that tungsten scrap is transformed into powder of the same composition by either chemical or physical treatment, or a combination of both. A typical example of the direct methods is the zinc treatment method. This method has many advantages, such as limited energy consumption and chemical waste, as well as low production costs. The disadvantages of this method are the restrictions on the recycled materials. The indirect methods, such as the wet chemical treatment method, are generally used in the ore refining process. This way of recycling has no restrictions on materials, but large quantities of chemicals and energy are needed.
Methods for recycling tungsten can be broadly divided into two types: direct methods and indirect methods. Direct methods mean that tungsten scrap is transformed into powder of the same composition by either chemical or physical treatment, or a combination of both. A typical example of the direct methods is the zinc treatment method. This method has many advantages, such as limited energy consumption and chemical waste, as well as low production costs. The disadvantages of this method are the restrictions on the recycled materials. The indirect methods, such as the wet chemical treatment method, are generally used in the ore refining process. This way of recycling has no restrictions on materials, but large quantities of chemicals and energy are needed.- The rise of the recycling industry
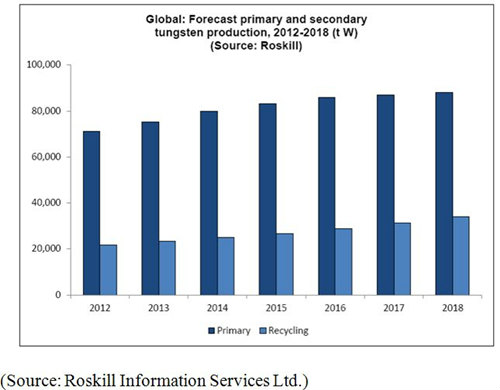
- The estimated increases in primary mine supply are predicted to be outpaced by the use of secondary recycled tungsten raw materials in the years to 2018. Tungsten recycling is expected to keep growing at about 8% per year over the next five years, increasing global production of recycled tungsten materials from 23% of total supply in 2012 to 28% of global supply in 2018. The main regions for growth in tungsten recycling are most likely to be Europe and Asia, as collection programs for tungsten products are improved and construction of new tungsten recycling facilities, particularly in China, are completed.
-
About us
Contact us
Make a suggestion
- Metalpedia is a non-profit website, aiming to broaden metal knowledge and provide extensive reference database to users. It provides users reliable information and knowledge to the greatest extent. If there is any copyright violation, please notify us through our contact details to delete such infringement content promptly.
 There are several reasons for recycling tungsten scrap. First, most scrap materials are richer in tungsten than ore concentrations, making tungsten scrap a worthy material for recycling. Second, the demand for tungsten products is increasing; consequently, the demand for tungsten resources is rising. Companies can lower their raw material costs and make greater profits by recycling tungsten scrap. Third, recycling tungsten scrap has many environmental benefits, such as reducing land-filled waste, saving valuable and finite virgin raw materials and energy, as well as reducing pollution.
There are several reasons for recycling tungsten scrap. First, most scrap materials are richer in tungsten than ore concentrations, making tungsten scrap a worthy material for recycling. Second, the demand for tungsten products is increasing; consequently, the demand for tungsten resources is rising. Companies can lower their raw material costs and make greater profits by recycling tungsten scrap. Third, recycling tungsten scrap has many environmental benefits, such as reducing land-filled waste, saving valuable and finite virgin raw materials and energy, as well as reducing pollution. Methods for recycling tungsten can be broadly divided into two types: direct methods and indirect methods. Direct methods mean that tungsten scrap is transformed into powder of the same composition by either chemical or physical treatment, or a combination of both. A typical example of the direct methods is the zinc treatment method. This method has many advantages, such as limited energy consumption and chemical waste, as well as low production costs. The disadvantages of this method are the restrictions on the recycled materials. The indirect methods, such as the wet chemical treatment method, are generally used in the ore refining process. This way of recycling has no restrictions on materials, but large quantities of chemicals and energy are needed.
Methods for recycling tungsten can be broadly divided into two types: direct methods and indirect methods. Direct methods mean that tungsten scrap is transformed into powder of the same composition by either chemical or physical treatment, or a combination of both. A typical example of the direct methods is the zinc treatment method. This method has many advantages, such as limited energy consumption and chemical waste, as well as low production costs. The disadvantages of this method are the restrictions on the recycled materials. The indirect methods, such as the wet chemical treatment method, are generally used in the ore refining process. This way of recycling has no restrictions on materials, but large quantities of chemicals and energy are needed.
