- As the lead industry is continuously improving, consumption of raw lead is increasing. Therefore, lead recycling has now become the focus for the industry. However, not all waste lead can be recycled - for instance, cable sheaths and lead pipes with a life span over several decades cannot be recycled. Meanwhile, the battery industry, as the main industrial application of lead, produces materials with a life span of 5-15 years, and is developing so rapidly that the room for lead recycling is very large.
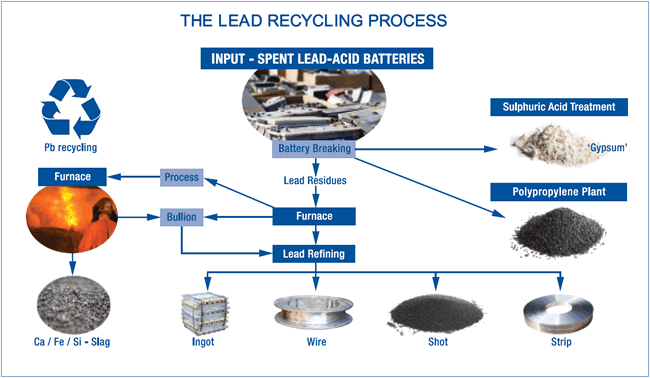
- Source: http://www.berzelius.de/ecobat/rp/-ECOBAT Technologies
- Lead recycling has the following benefits:
- More cost-effective
- Recycled lead is cheaper to produce than virgin lead. Recycled lead takes less than 25% of the energy required to produce lead from ore extraction.
- Conserves resources
 Recycling of lead has a smaller carbon footprint than mining, conserves ore reserves, and reduces the amount of waste associated with primary extraction.
Recycling of lead has a smaller carbon footprint than mining, conserves ore reserves, and reduces the amount of waste associated with primary extraction. - Benefits human health
- A high recycling rate means that there is less opportunity for lead to end up in the waste stream where it would pose a health risk to people. In recent decades, the amount of lead from batteries ending up in landfills has dramatically decreased, and as a result, the overall flow of lead to landfill has dropped markedly.
- Reduces strain on landfills
- By keeping lead out of landfills, recycling helps conserve them, and reduces the need for investment in controls to eliminate airborne particulates from incineration.
- Source: http://recycling.about.com/od/Recycling/a/Lead-Recycling.htm
- Currently, in industrialized and secondary development countries, secondary lead production now exceeds primary lead production. For instance, secondary lead production accounts for over 70% of the lead, total Europe has reached 80%, some countries with a shortage of lead resources have reached more than 90%, and the global average is 50%.
- Lead-acid batteries are by far the most fully recycled of all consumer products. Recycling centers can recover more than 97 % of the lead and plastic in a lead-acid battery. Once those reclaimed materials reach a battery manufacturer, they can account for 60-80% of the lead and plastic in a "new" lead-acid battery. It's a closed-loop lifecycle that can continue indefinitely.
-
About us
Contact us
Make a suggestion
- Metalpedia is a non-profit website, aiming to broaden metal knowledge and provide extensive reference database to users. It provides users reliable information and knowledge to the greatest extent. If there is any copyright violation, please notify us through our contact details to delete such infringement content promptly.

 Recycling of lead has a smaller carbon footprint than mining, conserves ore reserves, and reduces the amount of waste associated with primary extraction.
Recycling of lead has a smaller carbon footprint than mining, conserves ore reserves, and reduces the amount of waste associated with primary extraction. 